Fungal Infection of the Nails – Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
If you’re looking for information about the causes, symptoms, and treatment of fungal infections, this article is for you. Here, you’ll find information about Fungal Infection of the Nails. This infection is a common problem. It can cause painful symptoms and require medical treatment to treat. But don’t worry; there is treatment! Read on for helpful information about Fungal Infection of the Nails. In this article, you’ll learn what causes this condition, how to treat it, and which treatment is best for you.
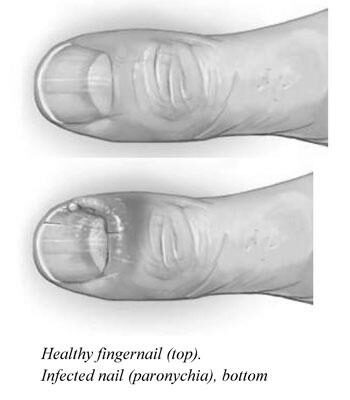
Fungal infection of the nails
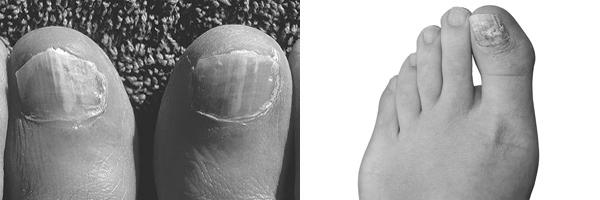
People who are elderly and have certain diseases with a weakened immune system are more likely to get a fungal nail infection. Additionally, those with diabetes and AIDS are also at a higher risk. People who take certain medications, such as steroids, may also be susceptible. While nail fungus is not highly contagious, it can be transmitted through constant contact. For this reason, people with diabetes or an immune system disorder should also seek medical advice for fungal nail infections.
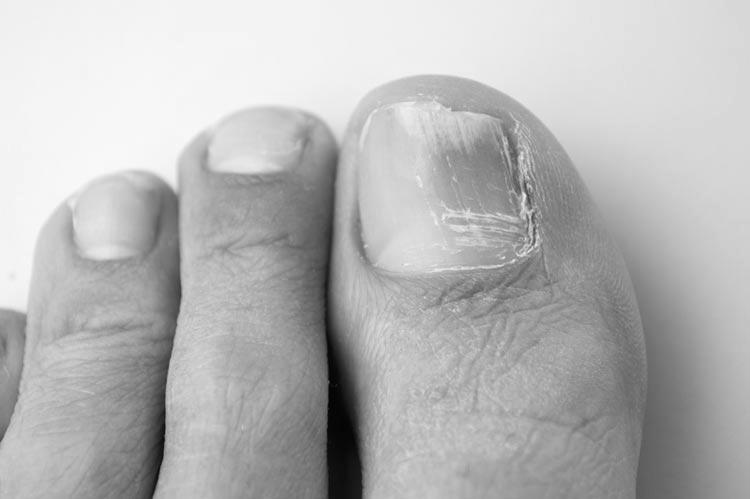
Symptoms of a nail fungus infection vary but are generally characterized by yellowish patches at the nail base. The disease may spread upwards as the yellow patches spread. People who constantly contact water or frequently use their nails may experience this infection. As the infection spreads, it may cause a partial or complete nail loss. If you are experiencing any of the symptoms listed above, you should visit a dermatologist as soon as possible.
The treatment of fungal infection of the nails is usually not practical, despite over-the-counter medications. In some cases, it is necessary to have a nail-pierced or surgically removed to cure the underlying fungal infection. However, these solutions usually only relieve symptoms and are not permanent. Moreover, fungal infections of the nails can lead to other health complications. Therefore, it is essential to seek medical attention if you notice symptoms of the condition.
The infection may be caused by fungus in the skin. Infections caused by fungus are more likely to happen in toenails than in other body parts. Nail fungus tends to occur more frequently in adults and older people. Older adults are especially at risk since their nails naturally grow slower. The symptoms can range from a mild infection to a painful one. It can also lead to ingrown toenails.
The infection of the nails can be challenging to treat, and complete clearance is not possible. Recurrence of the disease is common, and prevention measures include keeping your hands and feet clean and dry. Also, avoid sharing nail clippers and files with others, and wear socks with good ventilation. It is essential to wear shoes that keep the feet dry. You should also avoid walking barefoot in damp communal areas. So, how do you treat fungal infections?
The most common form of nail fungus is tinea unguium. Some people may experience symptoms like thickening or discoloration of their fingernails. A physician can help you get a proper diagnosis and treatment. For many people, treatment may include a prescription of antifungal medications. If the infection is severe enough, it can spread to the skin and fingernails. Once diagnosed, it may be necessary to get a nail fungus removed.
Causes

Fungal infections of the nails are caused by different species of fungi. These organisms infect the nail matrix, nail bed, and nail plate. While fungal infections often have a cosmetic impact, they can also be painful and cause functional impairment. In addition, fungal infections are associated with a stigma that can limit a person’s activities and quality of life. Here are some possible causes of nail infections and treatments for them.
The most common dermatophyte-caused nail infection is called DLSO. It is more common in toenails than in fingernails, and it begins as a fungus invasion. Infected nails become thick, discolored, and may exhibit varying degrees of onycholysis. The nail plate is not affected initially, but the infection can spread to the whole nail bed. Diseases of the nail plate can be treated with topical steroids and fusidic acid, which inhibits the synthesis of proteins by the fungal infection.
While there are many other nail infection causes, one of the most common is Candida. Candida infection accounts for five to ten percent of all cases of onychomycosis. There are different types of Candida infection, including distal onychomycosis and chronic mucocutaneous candidosis. The nail plate of fingernails is usually affected more than the toenails, but the middle finger and fourth finger are less likely to be infected.
Fungal infections can be caused by constant exposure to water. This condition is characterized by pus or blisters near the nail and can be transferred to other body parts. Among these nail infections causes are diabetes, fungi, and excessive sweating. If the condition is exacerbated by diabetes, treatment should focus on the underlying health condition. You should also avoid wearing shoes with pointed toes. It is essential to wear socks made of 100% cotton.
Another common cause of nail infection is chronic or repetitive trauma to the nail plate. This condition can cause the nail to become thick and discolored, which may prevent the wear of shoes and other footwear. In severe cases, the nail may break off and crumble. When the infection worsens, the nail can become crumbly and white spots may appear on the nail’s surface. Antifungal medications and surgery are often required to treat the disease.
If you have diabetes, you should also check with your doctor about possible fungi. Fungal infection of the nail is more common in older adults. As nails age, they become dry and brittle, allowing fungi to invade. A weakened immune system and reduced blood circulation in the feet may also lead to toenail fungal infection. Toenail fungi are commonly caused by various fungi, including psoriasis and molds.
Treatment
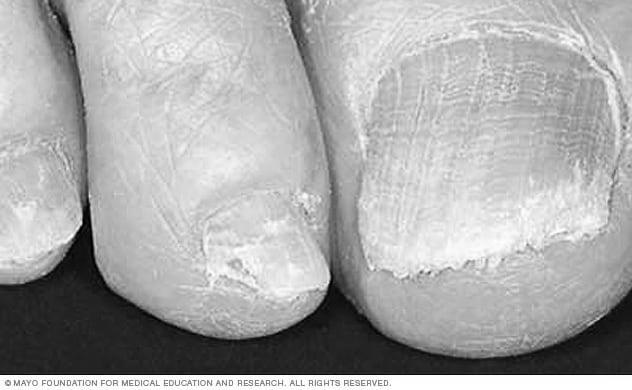
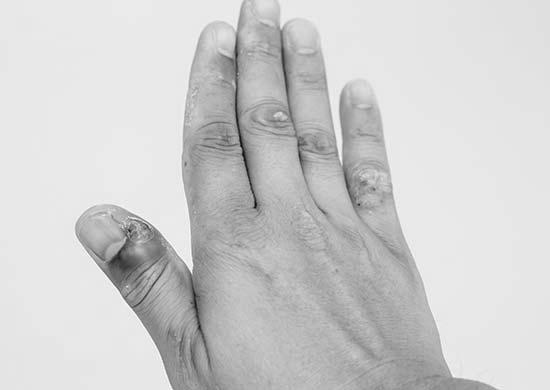
While most nail infections resolve on their own, some can be more severe and require medical attention. While a mild case of paronychia may be easy to treat at home, more severe infections can be complicated to treat and may even spread to other body areas. In such cases, professional treatment is the best way to go. Here are some tips for treatment:
Yeast onychomycosis (also called thrush) is caused by a type of yeast called Candida. It grows best in a warm, moist environment. Most cases occur in older adults because their nails grow slowly and have less blood circulation. Fungal infections can also be exacerbated by footwear, activity, and trimming of nails. While many fungi affect nails, Trichophyton is the most common. It causes various symptoms that vary depending on the type of infection.
Your doctor will probably recommend an oral antifungal drug to clear up the infection quicker than a topical solution to treat fungal nail infection. Itraconazole (Sporanox) and terbinafine (Lamisil) are common oral medications used to treat nail infections. When applied correctly, these drugs kill the fungus and promote the growth of new nails that are free of disease. These drugs also treat the skin underneath the nail.
Another option for treatment for nail infection is tioconazole, a prescription medication. It is an imidazole derivative with a broad spectrum of action. It is applied directly to the affected nail, usually twice a day. Patients with liver disease should seek medical advice about this drug since it may interact with other medications. This option requires weekly blood tests. It is a popular treatment for onychomycosis.
Laser treatments can also be used to remove the infected nail. These laser treatments are quick and relatively painless. Depending on the severity of the infection, one session can clear up the infection. However, for chronic cases, a doctor may recommend surgical removal. The nail might grow back healthy if it was removed surgically. However, the fungus is very stubborn, and a 40% recurrence rate can be expected. For best results, wash and dry your feet thoroughly after exposure to warm water. Additionally, it is essential to disinfect nail clippers and home pedicure tools to avoid causing further infection.
Another option for treatment for nail infection is an oral antifungal medication. A physician usually prescribes, and it takes nine to 12 months to fully cure the disease. Unlike topical treatments, oral treatments can have side effects and are time-consuming. Additionally, some people may not be able to take oral medications due to a condition that requires them to be on continuous medication. This is why a doctor should discuss your treatment options with you.
Why Are the Sides of My Nail Yellow?
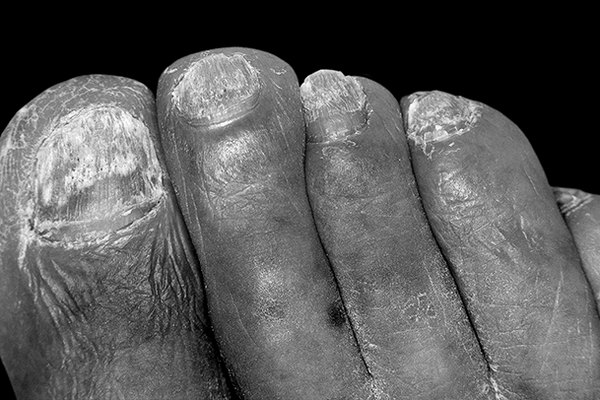
There are various reasons why your nail may be yellow, including the use of dark nail polish and fungal treatments. Thankfully, these issues aren’t permanent. You can treat the problem at home or seek a doctor’s advice. If you’re concerned, read on to learn how to cure yellow nail side effects. Or, get the treatment you need to get your nails back to normal!
Onycholysis
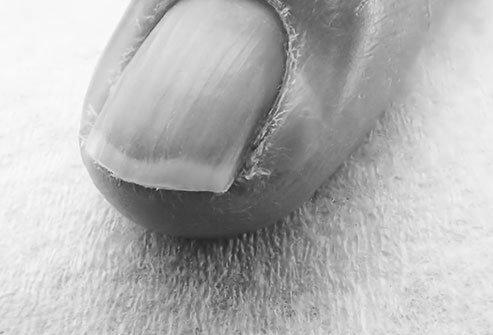
If your fingernails or toenails turn yellow, you may have a fungal infection. Fungal infections are commonly associated with thickened, crumbling nails and nail bed retractions. The side of your nail can also be bluish or yellow, indicating a problem with the blood vessels of the respiratory system. Blue and yellowish nails can also be symptoms of serious health problems, including lung and thyroid conditions and diabetes. Seeing a doctor is the best way to rule out a severe health problem or determine whether the infection is caused by something else.
A variety of chronic medical conditions can cause the sides of your nail to turn yellow. Specific color changes in nails may indicate diabetes, liver or kidney disease, heart or lung disease, or even a fungus. A dermatologist can culture your nails to identify the specific fungus and tailor a treatment for you. If the symptoms are not severe, topical antifungal medication may be sufficient. Rarely a genetic condition can lead to a yellow nail. Yellow nail syndrome is an inherited condition that results in yellowing the nail’s side. It is associated with diseases of the lungs and lymphedema.
The best way to treat yellow nails is to visit a dermatologist for a diagnosis. You should also consult a doctor if you notice the problem persists or if the yellowing becomes painful or bothersome. Using the proper medication is essential, but remember to remove the polish regularly to avoid worsening the situation. This will allow your nails to grow more vital and more vibrant. The right nail color will also make them more resistant to yellowing.
In some rare cases, the sides of your nail may be turning yellow. This is known as yellow nail syndrome, and it can signify a fungal infection. A dermatologist will be able to diagnose the condition through a series of tests, including a thorough physical exam and detailed clinical history. Then, they’ll refer you to a specialist who can treat your yellow nails.
Onychomycosis
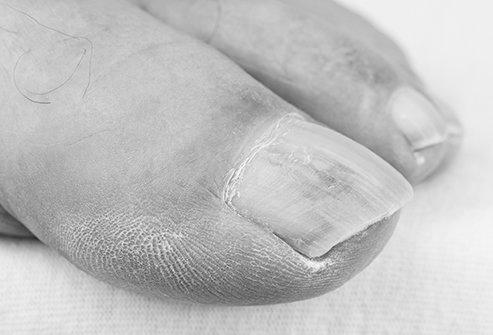
In rare cases, yellow nail staining is caused by applying nail polish or acetone-based nail polish removers. The resulting stain is harmless and cosmetic in nature. If you notice your nails becoming yellowish, visit a doctor.
Other potential causes of yellow nail color are tobacco, henna, and tanning products. An in-depth history of your exposure to these products will help you identify the culprit and prevent further nail discoloration. In the meantime, you should try not to use any of these products for at least three to six months. Also, you should avoid smoking. Some common conditions that cause yellow nails include diabetes and thyroid conditions.
The leading cause of yellow nail syndrome is an infection of the nail or surrounding skin. This infection often manifests with yellow sides and a foul smell. If left untreated, it can cause the nail to thicken and crumble. If you suspect a fungal infection, visit a doctor as soon as possible for a proper diagnosis and treatment. If the condition is caused by a fungus, you should see a dermatologist as quickly as possible. A doctor can recommend an antibiotic to treat the infection.
If you suspect you have a medical problem, visit a dermatologist to find a treatment for yellow nails. A dermatologist can help you determine whether you’ve contracted an infection or have a vitamin deficiency. A professional manicure can restore your nails to a healthy state. You should also be sure to avoid over-applying nail polish for several weeks. You should avoid covering your nails at first signs of yellowing.
There are several ways to treat fungal infections, including over-the-counter antifungals and removing the affected nail. Another treatment is using oregano oil, which is antimicrobial and kills fungi and bacteria. Apply oregano oil to the discolored nail. Ensure to dilute the oil in a carrier oil to get the best results. You can also try using tea tree oil.
Age-related yellowing
The causes of age-related yellowing of the sides of the nails are varied, but in general, there is no single cause. It is thought that yellow nail syndrome is caused by a malfunction of the lymphatic system, which filters and distributes protein-rich fluid through the body. In this syndrome, lymphatic fluid tends to collect in soft tissues, often under the skin, because of obstruction. In some cases, abnormal leakage of the small lymphatic vessels may also contribute to yellow nail syndrome.
Other possible causes of age-related yellowing of the sides of nails are medications and vitamin deficiency. If the sides of your nails have yellowed due to certain medications, you should visit a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis. The treatment for age-related yellowing of the sides of nails depends on the type of fungus. A dermatologist can culture your nails to determine the cause of the discoloration and prescribe appropriate medication.
Other causes of age-related yellowing of the sides of nails include rheumatoid arthritis and lung diseases. A yellow pin can also be an early sign of a severe infection, which requires treatment. Lines and deep grooves in the nail’s length are signs of slow nail growth, and a gap in the pin could indicate a complete stoppage of growth. Eventually, the nail may become missing, a condition known as onychomadesis.
Some of the causes of age-related yellowing of nails are fungal infections, a reaction to nail polish, or infection. Occasionally, the yellowing of a fingernail may signify a more severe condition, such as a bacterial or fungal infection. In some cases, a yellow nail can indicate lung disease, a lymphatic obstruction, or an internal malignancy.
Anemia, liver and kidney disease, and cancer are all possible causes. While most of these conditions can be treated quickly and effectively, it is best to see a physician as soon as possible. Your primary care physician is familiar with age-related nail disorders and can refer you to a specialist. However, if symptoms persist, the best place to begin treatment is with your family physician. It is not uncommon for patients to develop yellowing on the sides of their nails due to an underlying medical condition, such as diabetes or a thinning of the skin.
Fungal infection
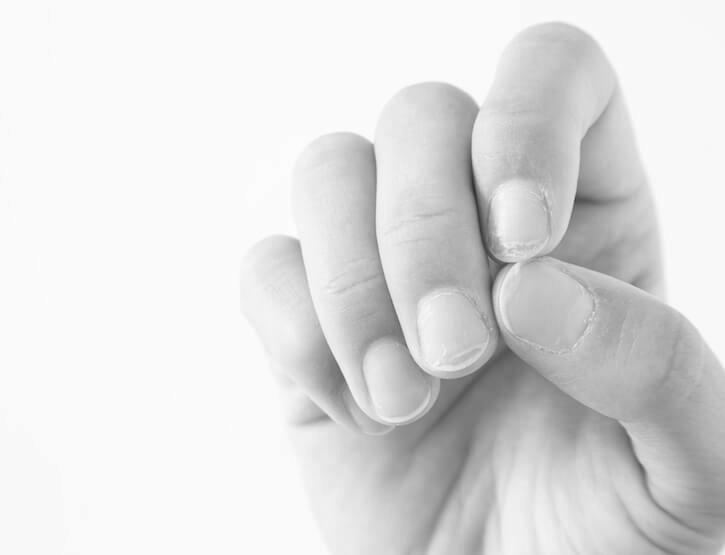

Besides the athlete’s foot, a fungus can also cause fungal infection on your fingernails. The symptoms of this condition may vary depending on the severity. If severe, they may even lead to thickened and deformed nails. This condition primarily affects toenails but can also infect fingernails. A fungus is caused by bacteria and is not dangerous, but it can cause severe itching and cracked skin around the nail.
While you can try home treatments for fungal infections, you can also visit a doctor. Your healthcare provider will prescribe medication that can help you cure your condition. Over-the-counter nail care products are available at your local pharmacy, but their results are mixed. Many sources claim that they cure fungal infections in days, but this is not true for everyone. There are many causes of thick yellow toenails, and there are no one-size-fits-all cures.
Treatment for a fungus infection depends on the severity of the problem and its location. Over-the-counter creams and solutions contain clotrimazole and undecylenic acid. Topical solutions such as Vicks VapoRub and eucalyptus oil may also help treat this problem. However, they don’t cure the condition, and it can take months to a year to clear.
The fungus can also affect other parts of the body. If it spreads to the rest of the body, it can cause damage and discoloration to the fingers, feet, and even the toenails. Those with diabetes may be at greater risk of getting nail fungus if they have poor circulation and a weakened immune system. Those with diabetes are more susceptible to developing nail fungus and should seek medical attention for treatment. They should wash their feet frequently and consult a physician if they suspect a fungal infection.
Treatment options for this fungus include oral medications and topical treatments. Over-the-counter colorless nail polishes contain antifungal ingredients that inhibit the growth of fungi and kill their fungus. These treatments require a regular application for up to a year to get rid of the problem. Other medicines need to use nail fungus treatment sets that remove the infected part of the nail for two weeks.